Materials are Components used to make Products. Together with Labor and Machines, they are used to create Assemblies. In some cases, a single Material may be available in multiple options, such as different sizes, colors, or finishes. Rather than creating a separate Material for each option, you can create one Material with Variants to manage those differences under a single record.
The system comes preloaded with some basic Materials, and additional Materials with Variants can be added as needed.
Note: It is recommended to clone an existing Material that is similar instead of creating a new one from scratch. For more information on how to clone a Material, please see Cloning a Material.
Table of Contents
Creating New Materials with Variants
Navigate to Settings / Components / Materials.
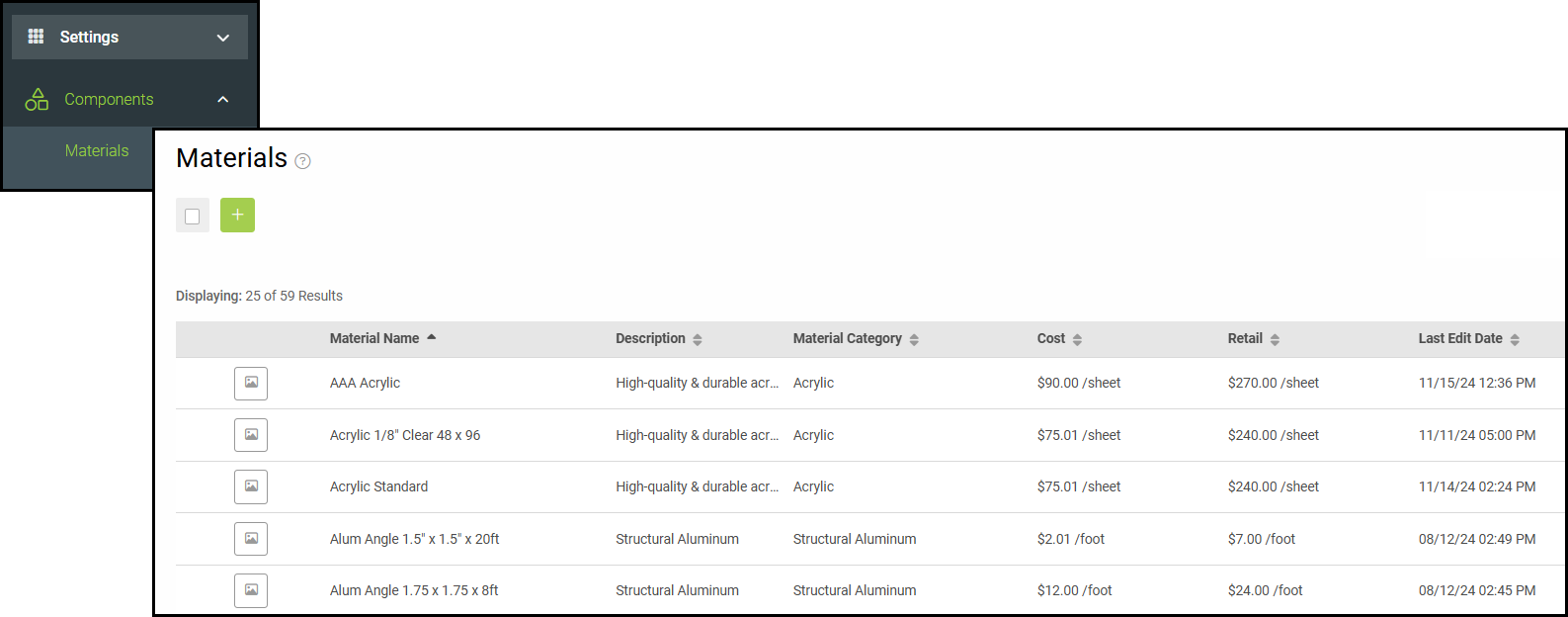
1. Select the Green Plus icon.
2. Select Material with Variants.

3. Enter the information about the material in the Details section.
Note: All fields with a red asterisk are required fields in order to save the material. Additional information will be needed for the material to be used in assemblies.
a. Name - This is the part name, it is recommended to start with the type of material then physical attributes, such as thickness, color, and sizes, as this will be listed in your material list using this name.
b. Name on Documents - This pertains to how this material will display on customer facing documents such as estimates and invoices.
c. Internal SKU - A unique Stock Keeping Unit used for internal inventory and tracking purposes if available.

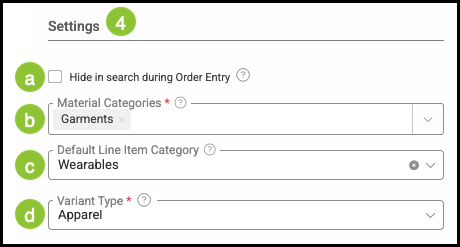
4. Enter the information about the material in the Settings section.
a. Selecting this option hides it from the available choices when adding Line Items during Order entry.
b. Material Categories - Categories help to organize the materials in the system. This list can be managed by clicking on Manage Material Categories in the dropdown if more categories are needed. For more information, please see Managing Material Categories.
Note: you can also add materials to categories under Settings / Components / Materials.
c. Default Line Item Category - This is an optional field used to organize components into common areas for better sorting and reporting options internally. Default Line Item Category can be managed in Settings / Sales / Line Item Categories.
d. A Variant Type is a predefined group that organizes the options available for a Material with Variants. Each Variant Type includes the Properties and Values a Material can use, such as color or size.
Note: Apparel is the currently available Variant Type. Additional Variant Types can be configured with assistance from support by reaching out to supportdesk@corebridge.net.
5. Consumption is how the material is consumed, rounded for usage, and scrap calculations.
a. Consumption Unit Type - By Area, Length, Discrete, or Countable Units.
b. Consumption Units - This is how this material will be consumed in production.
c. Round Up To - To the Next 10, Next Whole, or No Rounding.
d. Minimum Consumption in Each - Enter 0 unless a minimum amount of this material is used regardless of what the assembly calls for. such as .25 of a sheet, or feet off a roll every time.

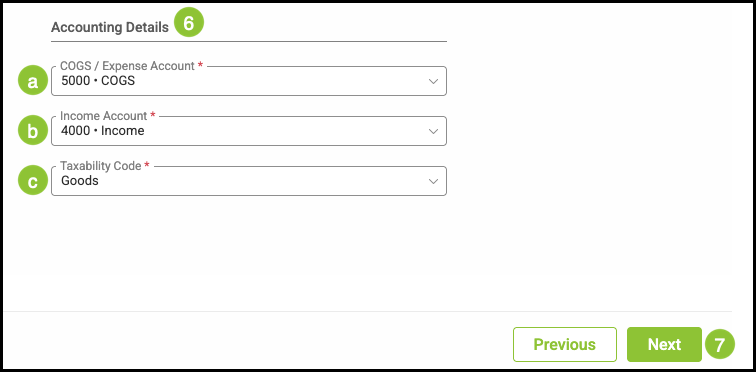
6. Accounting Details define how this material is categorized for billing, income, and tax purposes.
a. COGS / Expense Account - This is where the material cost will be accounted for, either in Cost of Goods Sold or the material is expensed.
b. Income Account - The income account when this material is sold.
c. Taxability Code - Goods, Service, or Tax Exempt material.
7. Click Next.
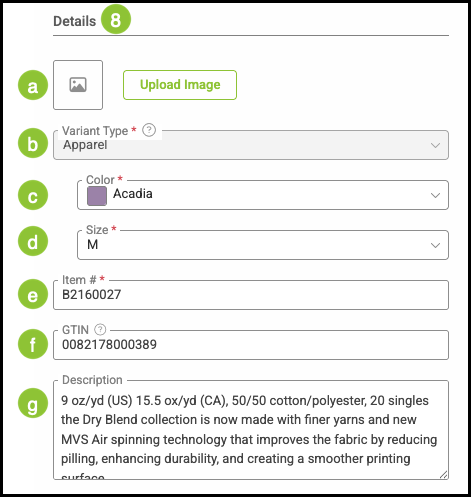
8. Enter the information about the material in the Details section.
Note: All fields with a red asterisk are required fields in order to save the material. Additional information will be needed for the material to be used in assemblies.
a. Upload Images of the material.
b. Name - This is the part name, it is recommended to start with the type of material then physical attributes, such as thickness, color, and sizes, as this will be listed in your material list using this name.
c. Name on Documents - This pertains to how this material will display on customer facing documents such as estimates and invoices.
d. Internal SKU - A unique Stock Keeping Unit used for internal inventory and tracking purposes if available.
e. A Global Trade Item Number (GTIN) is a universal identifier used to recognize the same Product across different brands and suppliers. Vendors may use their own item numbers, but the GTIN remains consistent.
f. Description - This is a broader description of this material for internal purposes.
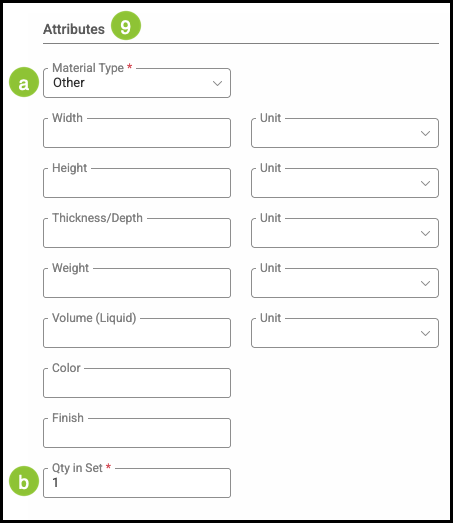
9. Enter the information for the Attributes.
a. The dropdown allows you to select the Material Type such as Roll, Sheet, or Other.
b. Qty in Set shows how many of this Material are sold in a set.
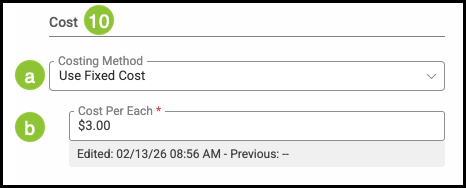
10. Enter the Cost information.
a. The Cost Estimating Method determines how the system calculates the cost of a Material.
b. Cost Per Each is the unit cost of a single item of this Material. This value is used in job costing and pricing whenever the Material is measured or sold per individual piece.
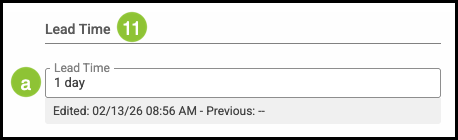
11. Enter the Lead Time.
a. Lead Time indicates the amount of time required to complete the Order from the point it is created.
12.Enter Retail Price details.
a. Retail Per Each is the price to the customer for just this Variant if purchased outside of an assembly.

13. Enter Custom Fields, if configured.
Note: For more information on Custom Fields, please see
14. Click Save and Continue.